Manual Mobile Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Smartphones literally dominate the world. There are 6.92 billion smartphone users in the world today, which is 85.88% of the world population. That figure is only 49.40% in 2016. Such ubiquity of smartphones demands mobile app developers to deliver high-quality applications at all times to remain competitive and relevant through effective mobile application testing.
In this article, we will take a deep-dive into the process of manual mobile application testing and see how teams should embrace a hybrid approach to receive the best of both worlds.
What is Mobile App Testing?
Mobile testing, or mobile app testing, is the process of checking and validating all aspects of the mobile app to ensure that they work as expected. Any issues and defects found during the process are reported to the dev team to address immediately so that they will not slip into production.
Benefits of Mobile App Testing
1. Ensuring that app defects are timely addressed
Bugs cost money.
Modern applications are built from highly interconnected components that must work together seamlessly to deliver the final expected feature. One single bug impacting a crucial component may create a negative ripple effect to other components and break the entire app.
For applications in sensitive fields (medicine, law, finance, insurance, etc.), such bugs can have irreversible consequences. Good mobile app testing catches those bugs and prevents them from slipping into production.
2. Maintain and enhance app quality
The journey of developing a mobile application pose never-ending questions like:
- How can we improve our user experience?
- How do we know which areas to test?
- In which area should we optimize and allocate our resources?
- Is the user feedback on our app valid?
Testing answers those questions, so we can confidently and continuously improve our app thanks to insights from test results.
What is Manual Mobile App Testing?
When doing mobile app testing manually, human testers interact with the application manually just as an end-user would to check if the application delivers the expected functionality and performance. They don’t rely on help from any automated scripts or tools, but solely use their human capabilities to find bugs.
Why and When To Do Mobile Testing Manually?
Manual mobile testing is when a developer or tester runs an app and interacts with its features without using automation. For small projects, writing automation scripts can be overkill. Even in large-scale apps, like a banking app, testers often start with manual testing to determine what’s worth automating.
Why is Manual Testing Important?
- More human input: Humans can think creatively, exploring an app like a real user. This is essential for testing aspects like UI aesthetics and navigation, which automation can't accurately assess.
- Finds new bugs, not just checks for them: Automation only verifies expected outcomes. Manual testing allows testers to experiment with different interactions, uncovering unexpected bugs.
- Lower learning curve: No coding expertise is needed—just a tester’s intuition and creativity to find ways to "break" the app.
- Lower maintenance cost: Automation scripts need updates whenever the app changes. In fast-paced Agile environments, manual testers can adapt immediately without reworking scripts.
Manual testing isn’t just a step before automation—it’s essential for real-world, flexible, and creative testing.
See How You Can Do Mobile Testing Without Code
Manual Mobile Testing in Different Test Environments
1. Emulators and Simulators

Emulators replicate both hardware and software, while simulators replicate only software.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Cheaper than buying multiple real devices, ideal for teams with limited budgets.
- Easily Available: Quick to set up and accessible within development tools like Xcode and Android Studio.
- Simple Setup & Tracking: Integrated into development environments, making test tracking easier.
- Parallel Testing: Run multiple tests simultaneously on different device configurations.
- Consistent & Repeatable: Provides a controlled environment for reliable test results.
Disadvantages:
- Lacks Real-World Accuracy: Doesn’t fully mimic real device behavior, leading to potential discrepancies.
- Hardware Limitations: Can't accurately test GPS, camera, sensors, battery life, or network conditions.
- UI/UX Testing Gaps: Can’t replicate real device responsiveness, touch sensitivity, or button feedback.
To test on emulators/simulators, you can:
- Set up and configure the emulator/simulator for the target platform (e.g., Android or iOS) on your development machine. You can use Android Virtual Device (AVD) Manager for Android or Xcode for iOS emulators. Emulators are more commonly used in Android while simulators are usually specific to iOS.
- Start the emulator/simulator, which will run a virtualized version of the mobile operating system
- Install the mobile app you want to test on the emulator/simulator. You can often drag and drop the app's installation file (APK for Android or IPA for iOS) onto the emulator.
- After that, you can start testing. Use the emulator's interface to interact with the app just like you would on a physical device. You can click, swipe, enter text, and perform any actions you need to test the app's functionality.
Read More: Mobile Emulator vs Simulator vs Real Device: Key Differences
2. Real device cloud
A “real device cloud” is a cloud-based platform providing access to a wide range of physical mobile devices for testing and development purposes.
You can choose between a lot of makes, models, OS, screen sizes, and even network configurations on these clouds. Even better, users can access and control those physical devices remotely through the web.
Real device cloud gives testers a much more comprehensive testing experience. For mobile applications with a diverse user base, or having specific hardware requirements, this is a great option compared to emulators/simulators.
For example, with Katalon TestCloud, you can gain access to mobile test environments to execute your tests without having to buy any physical machines or set up local emulators/simulators. Katalon TestCloud allows you to run tests on mobile browsers as well as for mobile native applications.
To get started, create your free Katalon account. You should get access to the Katalon TestCloud and Katalon Studio.
Katalon Studio allows you to create mobile test cases by drag-and-dropping uilt-in Keywords (which are essentially code snippets) or record your on-screen actions and turn them into a test script. In other words, you don’t need to have coding experience to create tests for mobile apps in Katalon Studio.
You can then click on the Run icon to select where you want to run your mobile tests. Choose TestCloud to execute tests on common browsers and operating systems on the cloud.
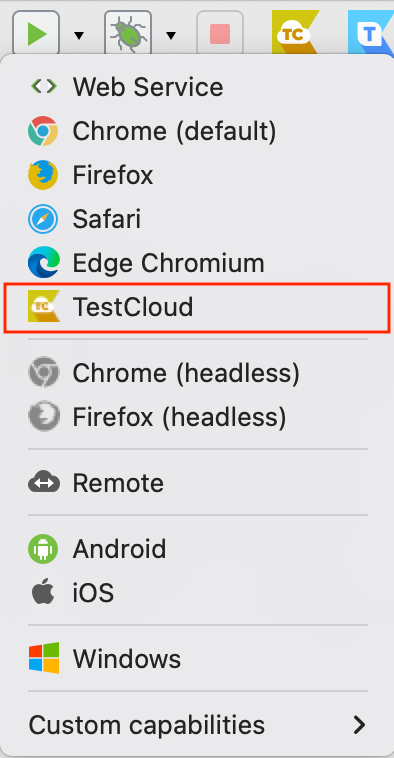
Here you can choose the specific device, OS, version, and browser you want to run your test on. After everything is fully configured, simply click “Run”.
Real device cloud is invaluable for ensuring the quality, compatibility, and reliability of mobile applications across a wide range of real-world devices and conditions.
Start Mobile Testing With Katalon
3. Test on real devices
Testing on real devices simply means executing your tests on actual physical devices rather than using emulators, simulators, or virtual environments. The obvious advantage of this approach is its level of realism. Real devices provide the most accurate representation of how an application will perform in real-world scenarios.
However, access to a wide range of real devices is challenging. Purchasing the devices is only the first stage. Organizations also need to maintain and manage them, and over time this can compound into enormous cost, which is not at all ideal for smaller teams.
Real device testing is also constrained by environmental factors, such as physical device availability, testing space, and the need for manual intervention.
How To Perform Effective Manual Mobile Testing?
1. Set A Clear Plan
Automated mobile testing involves creating test scripts that can be stored in the version control system, and its results are logged with detailed information about each step performed. For manual mobile testing, it is not that simple. Human testers have to manually test then manually document the results in a spreadsheet or a test case management system. This is why having a clear test strategy and test plan is especially important when testing mobile apps manually.
In a test plan, determine testing objectives, which allow you to better identify test scenarios and establish the potential test cases. Have a test case template to help you note down your test steps in a structured fashion. This should also help to standardize the testing process and improve test result consistency throughout many iterations.
Many manual mobile testers develop a click path to help them achieve that goal.
2. Have A Detailed Click Path

A detailed click path provides step-by-step instructions for navigating through the mobile app's user interface. This ensures that testers can reproduce the same sequence of actions consistently during testing, which is essential for reliable results.
Knowing what you are clicking on and where it is leading you to should also improve your test coverage. Compare your click path and the app architecture to identify areas that have not been adequately tested. The click path also makes it much easier to reproduce the bug, since you can just reverse the path from the breakpoint to the starting point. Developers can use that insight to find the root cause and fix the bug more easily.
Read More: Bug Life Cycle in Software Testing
3. Test On Multiple Devices and Environments
It is actually an ambitious endeavor to test all devices and environments there are, so QA teams usually deep-dive into analytics of their user base structure to identify which techstack app users tend to use to identify the devices and environments worth testing.
When talking about environments, we are also talking about network conditions. Certain applications provide both online and offline modes. Testing under different network conditions also provides insights into how the app consumes network data, and if any features cause slower-than-average loading time.
4. Choose Complicated Use Cases
Manual testing is the ultimate playground for testers. They don’t really have to follow a path as rigid as automated testing, so they can totally take advantage of this liberty to explore the more complex scenarios. Interestingly, a recent research shows that manual mobile testing catches bugs requiring 3+ interactions from users i.e. complicated bugs, while automated testing can only catches bugs requiring fewer than 3 interactions.
The power of testing manually does not stop there. This is an opportunity to check for UX-related issues, such as unintuitive workflows, confusing interfaces, or unexpected user interactions.
5. Leverage Ad-hoc and Exploratory Testing
Ad-hoc testing and exploratory testing are both popular manual testing techniques allowing testers to go beyond the “happy path” and discover bugs that they have never thought of before. Testers rely solely on their intuition, experience, and existing knowledge of the application to freely “explore” the system, trying combinations of interactions that can potentially lead to a bug. This degree of liberty is much harder to achieve in automation testing, so make sure to utilize it when doing manual mobile testing.
6. Document Testing Results
Finally, as we are doing everything manually, results must also be carefully documented in a spreadsheet for future analysis. For aspects of the bug that can be quantified, make sure to establish a structured framework for better bug understanding, future analysis, and troubleshooting. This is also known as the bug taxonomy.
Essentially, in a bug taxonomy, bugs sharing common attributes are organized into predefined categories. Below is a compilation of fundamental bug categories for your consideration:
- Severity (High - Medium - Low impact to system performance/security)
- Priority (High - Medium - Low urgency)
- Reproducibility (Reproducible, Intermittent, Non-Reproducible, or Cannot Reproduce)
- Root Cause (Coding Error, Design Flaw, Configuration Issue, or User Error, etc.)
- Bug Type (Functional Bugs, Performance Issues, Usability Problems, Security Vulnerabilities, Compatibility Errors, etc.)
- Areas of Impact
- Frequency of Occurrence
Best Practices For Testing Mobile Apps Manually
1. Choose the right platform
- Decide between Android, iOS, Windows, or web browsers based on your target audience and business goals.
- Each platform has different development requirements, user bases, and market share, so choosing the right one ensures better reach.
2. Understand your target users
- Testing isn’t just about fixing bugs; it’s about ensuring the app meets user needs.
- Consider demographics, preferences, and common frustrations to design a more user-friendly experience.
- A user-centric approach leads to better engagement and usability.
3. Prioritize functionality
- Test the app’s core functions first to confirm they work as expected.
- Since manual testing takes time, focus on high-impact areas before moving to minor features.
- Identify parts of the app that can be automated to save time, and use low-code automation tools or AI to assist without requiring deep technical skills.
Manual Mobile Testing FAQs
1. When should testers choose manual testing or automation testing for mobile testing projects?
- Choose manual testing when you want a human tester to interact with the mobile app, explore its user interface, and perform ad-hoc or exploratory testing. Manual testing is best for scenarios where frequent changes occur or when testing new features.
- Choose automation testing when you want to run repetitive tests quickly and consistently. Automation is ideal for regression testing, where you need to ensure that existing functionality isn't affected by code changes. It's also helpful for load testing and running tests on various devices simultaneously. Read More: How To Build A Regression Test Suite?
2. What are types of mobile app testing?
There are several types of mobile app testing, including:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that the app's features work as intended.
- Usability Testing: Focuses on the user experience, navigation, and ease of use.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates app speed, responsiveness, and resource usage.
- Compatibility Testing: Checks how the app behaves on different devices and operating systems.
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities and ensures data protection.
- Automation Testing: Involves using scripts to automate test cases.
- Load Testing: Measures app performance under heavy user loads.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensures the app is usable by people with disabilities.
3. How to create an effective mobile testing strategy?
- Define clear testing objectives and goals.
- Identify the target audience and devices.
- Prioritize testing based on critical features and user scenarios.
- Develop detailed test plans and test cases.
- Choose appropriate testing tools and frameworks.
- Conduct manual and automated testing as needed.
- Perform regression testing after updates.
- Continuously gather user feedback and adapt testing accordingly.
4. What are some best mobile testing tools/frameworks?
- Appium: An open-source automation tool for mobile apps.
- Katalon: going beyond just a mobile testing tool, Katalon also allows you to create, manage, execute, and report for tests on web, desktop, and API. It is a comprehensive solution for testing teams of any size. See how Katalon helps your team grow.
- XCTest and XCTestUI: Native testing frameworks for iOS.
- Espresso: A testing framework for Android apps.
- Calabash: An open-source tool for mobile automation.
- Selendroid: A framework for testing Android apps.
- TestComplete: A comprehensive testing tool for mobile and web.


