What is Automation Testing? Ultimate Guide & Best Practices
Software is so deeply integrated into our modern daily life. To ensure that these systems are always up and running, automation testing is needed.
Instead of manually clicking and checking for bugs, you can automate those activities by writing scripts to command the machine to perform those actions on your behalf. It significantly speeds up testing while freeing up bandwidth for testers to focus on strategic tasks.
Want to learn more about automation testing? This article’s got you covered!
What is Automation Testing?
Automation testing is the practice of using scripts and specialized tools to automate the execution of tests to check for issues in the system and ensure that it is working as expected.
Those automation scripts and tools directly command the Application Under Test (AUT) to perform all actions on behalf of the tester.
Thanks to automation testing, testers don’t have to manually interact with the system over and over, which is a time-consuming process. All they have to do is click the “Run” button, sit back, and let the script do the work.

Source: r/ProgrammerHumour
Is automation worth it? Yes, if the specific test case you are automating is highly repetitive. You’d be better off spending 1 hour scripting for a test that can then be automatically run hundreds of times than manually executing it hundreds of times all by yourself.
Manual Testing vs. Automation Testing
Simply put:
- Manual testing involves a human tester manually interacting with the system to find bugs.
- Automation testing involves writing a script to command the system to perform test steps for humans.
|
Aspect |
Manual Testing |
Automation Testing |
|
Execution |
Performed by human testers |
Performed using scripts and testing tools |
|
Speed |
Slower, requires human effort |
Faster, can run tests automatically |
|
Accuracy |
Prone to human error |
More precise and consistent |
|
Best For |
Exploratory, UI, usability testing |
Regression, load, and repetitive tests |
Benefits of Automation Testing
Automation testing is the best way to enhance effectiveness, broaden test coverage, and improve execution speed. Here are some of the obvious benefits you can get from automation testing:
1. Improved Accuracy
Automation testing eliminates human error by following exact, predefined steps every time, ensuring consistent execution without missed steps.
2. Increased Speed
Automated tests run 24/7 without breaks and can be executed in parallel, allowing dozens or hundreds of tests to run simultaneously, significantly reducing testing time.
3. Cost Savings
Although there’s an initial investment in creating and maintaining test scripts, the long-term benefits in speed, accuracy, and consistency lead to substantial savings, especially for complex projects.
4. Enhanced Test Coverage
Automated tests can be reused across multiple browsers, devices, and operating systems. Cloud environments make it easy to test on older versions as well.
5. Improved Test Reusability
Once automated tests are created, they can be reused in future test cycles. There's no need to recreate them—just run the existing scripts as needed.
6. Continuous Testing
Automated tests can be integrated into the development process, running automatically whenever new changes are made, ensuring ongoing quality checks throughout the pipeline. If you're a software business or an individual working in the digital industry, investing in automation testing will surely bring immense benefits to your product development process.
Learn More: Benefits of Automation Testing You Should Know
Which Test Cases To Automate?
Yes, automation testing is awesome, but not all tests can be automated. It’s all about “automation feasibility”.
So, what makes a test case feasible for automation? There are several:
- Tests that need to be run frequently and repeatedly
- Tests that require large datasets and many iterations
- Tests that take too long or just tedious when done manually
- Tests requiring execution on multiple hardware and software platforms
Before starting automation, make sure to go through this step. Striking a nice balance between manual tests for ad-hoc, non-repetitive test cases and automated tests for time-consuming, repetitive test cases is how you maximize test coverage.
With that in mind, here are the types of tests that should be automated:
- Smoke Tests – Basic checks to ensure core functionality works.
- Regression Tests – Verify that new changes don’t break existing features.
- Data-Driven Tests – Run the same test with different data sets.
- Unit Tests – Check individual components or functions.
- Cross-Browser Tests – Ensure the app works across different browsers and devices.
How To Do Automation Testing?
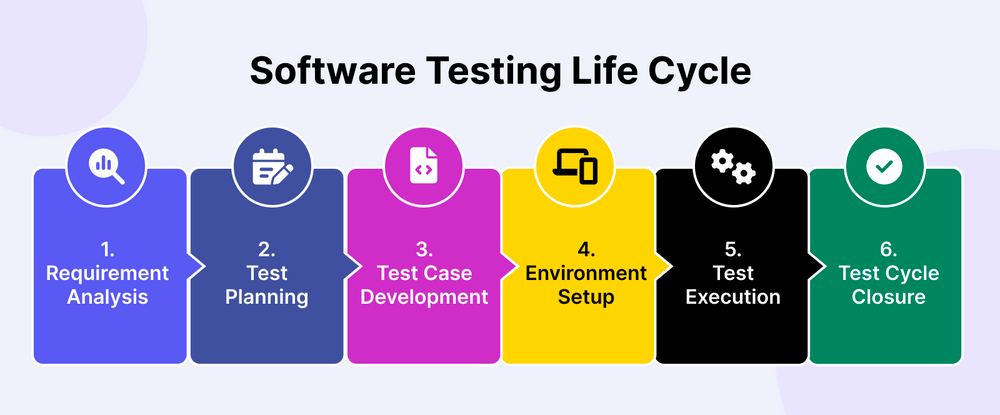
Testing, in general, follows the Software Testing Life Cycle, which consists of 6 stages:
- Requirement analysis
- Test planning
- Test case development
- Environment setup
- Test execution
- Test cycle closure
No matter if you’re doing manual testing or automation testing, these steps are always followed in one way or another. What sets automation testing apart is at the Test case development stage.
For manual testing, you list down the test steps and then manually execute it step-by-step. For automation testing, you go the extra mile of writing the test script, but only have to click the “Run” button to execute.
Step 1. Choose your approach
To do automation testing, you have 2 approaches:
- Use a test automation framework
- Use a test automation tool
Here is a comparison table for the pros and cons of each approach:
|
Aspect |
Test Automation Tool |
Test Automation Framework |
|
Level of Abstraction |
Offers a higher level of abstraction, allowing users to automate tests without extensive programming knowledge. |
Requires a certain level of programming expertise and understanding of coding principles. |
|
Learning Curve |
Typically has a lower learning curve, making it accessible to individuals with limited programming skills. |
May have a steeper learning curve, as it requires a deeper understanding of automation principles and programming concepts. |
|
Customization |
Provides limited customization options, as users are bound by the features provided by the tool. However, many tools do offer Scripting mode along with low-code mode to increase customization level |
Offers extensive customization and flexibility, allowing users to tailor the framework to specific project needs. |
|
Ease of Initial Setup |
Generally easier to set up, with user-friendly interfaces and wizards guiding users through the configuration process. |
May involve a more complex initial setup, requiring expertise in designing and structuring the framework. |
|
Resource Efficiency |
Tends to be more resource-efficient, making it suitable for smaller projects with limited resources. |
May be resource-intensive, requiring time, effort, and expertise. |
In other words:
- To best utilize a framework, you must have extensive coding knowledge yourself, and the effort to maintain test scripts is significant, but you can freely customize the framework to fit your specific testing needs
- A testing tool doesn’t require coding so you can easily create tests much faster. You can switch to coding mode whenever you want (if the tool offers coding mode). Test maintenance is usually taken care of, which reduces the workload. However, you are bound by the features offered by the tool, so it is recommended to list out the features you want from a tool to select the one that best fits your demands.
Step 2. Perform exploratory testing
If this is the first time you do automation testing for a certain system, you should first perform some exploratory testing to understand its features, so that you know what and where to test.
There is really no rule to exploratory testing. It all depends on your intuition, domain knowledge, and experience. Target high-risk areas such as complex features with intricate workflows, recently modified code, integration points, etc.
Ask yourself:
- What are the boundaries of this system? What happens when we push those boundaries? For example, what occurs if you input a username that is 10,000 characters long?
- What are the error messages? A system can work correctly in one way but fail in hundreds of ways. Focusing on these scenarios can uncover many unexpected bugs.
- What confusions have you encountered? If a certain area of the product seems confusing, is there something wrong with it?
Let’s Game It Out is a let’s play YouTube channel by a guy named Josh with chaotic evil energy. He embodies the exploratory testing spirit. Josh sets out to push every game he plays to its absolute limit and breaks the system. If you’re doing exploratory testing, do it like Josh.
Here's a fun video of how he breaks the game:
Once you have understood the system, you can start defining where to automate.
Step 3. Write the tests
Selenium and Cypress are two of the most popular automation testing frameworks out there. They support a wide variety of languages, so you can write in the one you feel the most comfortable with.
Here’s a simple Selenium script written in Python to launch a browser, navigate to a website, click a button, and check if a certain result appear.
from selenium import webdriver # Set up WebDriver (e.g., Chrome) driver = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path='path_to_chromedriver')
# Navigate to a website driver.get("https://testwebsite.com") # Interact with elements (find a button and click it) button = driver.find_element_by_id("myButton") button.click() # Check the result assert "Expected Result" in driver.page_source # Close the browser driver.quit()
To familiarize with the commands, simply go through their documentation.
With automation testing tools, you usually get a host of features to support your test writing activity. For example, in Katalon Studio, you can leverage the Record-and-playback feature to record on-screen actions and turn them into an automation test script.
You can also use the Built-in keywords from the Keyword Library. These keywords are basically just pre-written code snippets to automate specific actions. String these keywords together and you should have a full test script ready to be executed across any environment.
For example, for the same test script above, you can piece these keywords together:
- Open Browser (Chrome)
- NavigateToURL (https://testwebsite.com)
- Click (Element ID: myButton)
- VerifyElement (driver.page_source)
- CloseBrowser
Start Automation Testing With Katalon For Free
Step 4. Prepare test environment
There will be clear hardware-software specifications for any testing projects, and that includes requirements on servers, databases, OS, browsers, and any third-party tools needed to perform the test.
For example, if you want to test a Login page, you need to prepare:
- The browsers (Chrome, Safari, Edge)
- Devices in a wide variety of versions (desktop, tablet, laptop, mobile)
- Operating system with suitable versions
- Suitable network conditions
There are 3 types of environment you can go with:
- Run tests locally with your device being the environment itself
- Run tests remotely leveraging services like Selenium Grid or virtual machines
- Run tests on-cloud leveraging platforms like AWS DeviceFarm
Step 5. Execute tests & analyze results
With all test cases ready, you can start test execution and gather results.
Read More: Steps To Build A Good Automation Test Report
Challenges of Automation Testing
Of course, automation testing is not without its challenges. There is usually some compromise to be made when you want to increase testing speed. What’s important is whether that compromise is worth it or not.
According to the State of Quality Report 2024, the most prevalent challenge to automation testing is the team's lack of skills and experience in test automation, with up to 45% of respondents agreeing, followed by 38% thinking that requirements change too often, and another 26% claiming that test maintenance is costly.
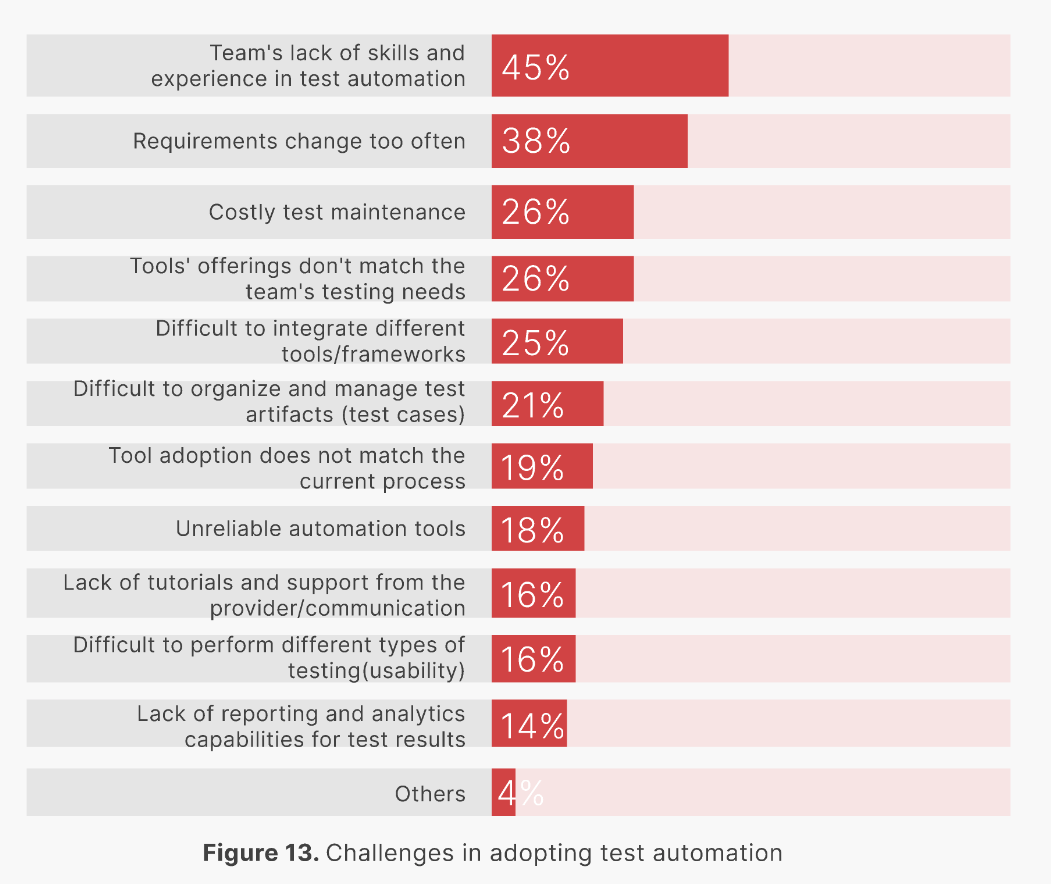
→ Download the State of Quality Report 2024 to get the latest industry insights
Automation Testing Best Practices
1. Start with High-Priority Tests
Begin by automating your regression and smoke tests. These are the most important, run frequently, and cover critical features that don’t change often. Automating them first saves time, reduces risks, and provides fast feedback on core functions.
2. Use Data-Driven Testing
Avoid hardcoding test data into scripts. Instead, separate test data from test logic. This makes your tests more flexible and reusable. Think of it like swapping outfits—you keep the core test and just change the data to run multiple scenarios easily.
3. Build Modular, Reusable Scripts
Write reusable scripts to avoid repetitive work. For example, if you have a login script, make it a module. Then, whenever a test requires login, reuse that module. This saves time, simplifies updates, and keeps your scripts cleaner and easier to maintain.
Read More: Top 6 Types of Test Automation Frameworks
4. Regularly Review and Update Tests
Automation isn’t a “set it and forget it” process. Software changes, so your tests must evolve too. Review and update tests regularly to keep them accurate, reliable, and relevant. It’s easier to fix small issues early than deal with major problems later.
5. Integrate with CI/CD Pipelines
Connect your tests to CI/CD pipelines to automate the whole process. Every time a developer pushes new code, tests run automatically and give quick feedback. Fast feedback leads to quicker fixes, smoother releases, and happier users.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, automation testing is a critical component of any software development process. With the right tools and approach, organizations can improve the speed and accuracy of their testing, catch bugs earlier in the development cycle, and ultimately deliver better products to their customers.
If you don't know which test cases to start with, here’s a list of popular test cases for you. They should give you a good foundation of how to approach a system as a tester.
- Test Cases For API Testing
- Test Cases For Login Page
- Test Cases For Registration Page
- Test Cases For Banking Application
- Test Cases For E-commerce website
- Test Cases For Search Functionality
FAQs On Automation Testing
1. What are the skills required for automation testing?
Automation testers need:
- Programming skills (e.g., Python, Java, JavaScript)
- Knowledge of automation tools (Selenium, Cypress, Appium)
- Understanding of test frameworks, CI/CD integration
- Problem-solving abilities
- Familiarity with version control and test management tools
2. What tool is used for automation testing?
Popular tools include:
- Selenium (for web applications)
- Cypress (modern web apps)
- Appium (mobile apps)
- Postman (API testing)
- Katalon (all-in-one automation testing solution)
- Jenkins (CI/CD)
- TestNG or JUnit (test management).
Each tool has their own pros and cons. Make sure to choose a tool based on your project needs.
3. How do you automate testing?
Automating testing involves:
- Choosing a tool that fits your application
- Writing scripts in a supported language (e.g., Java, Python).
- Integrating with CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing.
- Running tests and analyzing reports to identify issues.
4. Is automation testing a good career?
Yes, automation testing is a highly in-demand career with strong growth prospects. Companies are moving towards DevOps and Agile methodologies, making automation essential for faster, reliable testing. Automation testers are well-paid and have opportunities to work across various industries.
5. Does automation testing have a future?
Absolutely! Automation testing is the future of QA as it enables faster software delivery with higher accuracy. It’s evolving with AI/ML-based testing, self-healing tests, and cloud testing, ensuring long-term demand in the tech industry.


