50+ QA Interview Questions And Answers 2025
Interviews are anxiety-inducing, and nothing can better boost your confidence than some solid knowledge preparation before you enter the interview room. Here are top 50+ QA interview questions and answers for you to review your knowledge in Quality Assurance and the testing process.
We have categorized these QA interview questions by difficulty level, question types, and even positions (QA manager, QA lead, and QA tester). You may read through all 50 of these interview questions or jump to the most personally relevant sections. The choice is yours!
Common QA Interview Questions And Answers
1. What is Quality Assurance? Give a real-life example of quality assurance in software development.
QA in software development ensures software meets quality standards by testing functionality, performance, usability, and security.
For example, before launching a mobile banking app, the QA team checks if users can log in, view balances, transfer funds, and make payments. They also test how different code modules communicate in the back end.
If bugs are found, they report them to developers for fixing. Once resolved, QA retests to confirm the fix and ensure no new issues appear.
Read More: Software Quality Management Best Practices | 5 Do's & Don'ts
2. What is the software testing life cycle? Explain each step in the cycle.
The software testing life cycle is the standard process that software testing teams follow to ensure that software products are thoroughly tested and meet the specified quality standards.
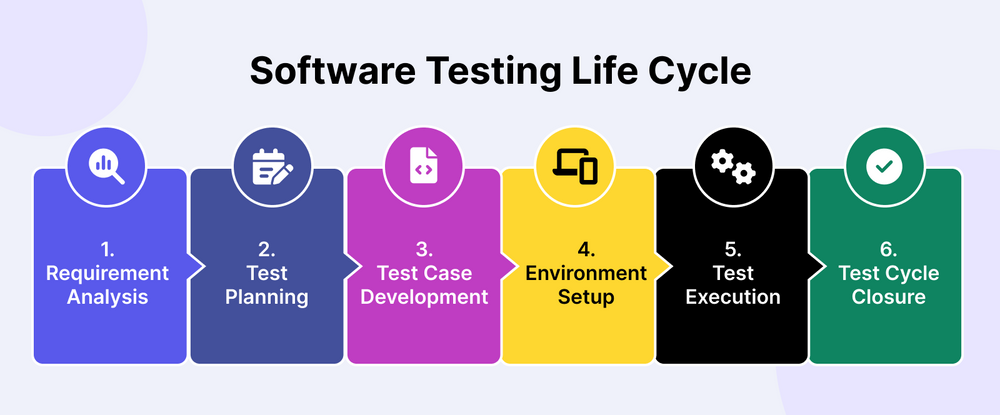
Here are the steps:
1. Requirements Analysis
- QA analyzes software requirements to create a test plan.
- Developers focus on translating requirements into code.
- Testers ensure testability by breaking requirements into test cases.
- Both teams collaborate to assess feasibility.
2. Test Planning
- Align with stakeholders on testing strategy.
- Define test objectives (functionality, usability, security, etc.).
- Outline test scope (what will/won’t be tested).
- Allocate resources (tools, testers, environments).
- Set timelines and milestones.
- Choose test approach (manual vs. automation, test types).
3. Test Case Development
- Write test cases based on planned scenarios.
- Use tools like Xray for manual testing.
- Automate tests with Katalon, Ranorex, or Selenium-based frameworks.
- Run tests manually or via automation.
- Set up testing environments (cloud or physical devices).
- Identify, track, and report defects for fixes.
5. Test Cycle Closure
- Review test reports, unresolved defects, and release readiness before deployment.
3. What is your experience with automation testing tools?
An automation testing tool helps teams write, run, debug, and report test scripts efficiently. It should also integrate with key DevOps tools like test management, defect tracking, CI/CD, and containerization platforms.
Test automation tools are categorized based on:
- Application Type: Web, mobile, API, or desktop applications.
- Application Layer: UI testing vs. API testing.
Some of the common names by application types are:
- API and web services testing: Postman, Katalon, SoapUI
- Web UI testing: Katalon, Ranorex, TestComplete, Cypress
- Mobile testing: Appium, XCUITest, Katalon, TestComplete
4. Explain the different test levels of and give examples

Testing levels refer to the different stages and granularity of testing.
Let’s use an ecommerce website to give sample scenarios for unit testing, integration testing and end-to-end testing.
- Unit testing: tests the login page to handle valid/invalid credentials (usernames, passwords)
- Integration testing: tests the payment processing process where Paypal can verify payment details like valid card numbers
- End-to-end testing: tests the series of actions to place an order (update inventory > send order confirmation email > process payment > updating order status) as a whole
5. What is your approach to test planning?
We can approach test planning through 3 major approaches: risk-based, model-based, or hybrid.
Risk-Based Test Planning
- Prioritizes testing efforts based on the potential impact and likelihood of defects.
- High-risk areas get more testing, while low-risk areas receive minimal effort.
- Example: A banking app prioritizes security and transaction features over UI cosmetics.
Model-Based Test Planning
- Uses models (diagrams, workflows, state transitions) to design and automate tests.
- Helps visualize complex systems and generate test cases systematically.
- Example: A chatbot system is tested using a state-transition model to cover different conversation flows.
Hybrid Test Planning
- Combines multiple test approaches (e.g., risk-based + model-based) to optimize coverage.
- Flexible and adaptable to different project needs.
- Example: A healthcare app applies risk-based testing for security while using model-based testing for patient data workflows.
6. What is exploratory testing?
Exploratory testing is a testing approach that involves simultaneous learning, test design, and execution. It is employed when there is no formalized test plan or script, and when there is a need to discover issues not yet covered by existing test cases.
Exploratory testing is typically performed by experienced testers who use their domain knowledge, intuition, and creativity to identify defects in the software.
Read More: Exploratory Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
7. Explain stress testing, load testing and volume testing?
Stress Testing – Pushes the application beyond its limits to see how it breaks. This helps developers prepare for failures and improve system resilience.
- Example: Simulating a sudden surge in users during a big sale.
Load Testing – Tests the system under expected user traffic to find performance issues like slow response times or high CPU usage.
- Example: Checking if an e-commerce site can handle thousands of users browsing at once.
Volume Testing – Assesses how well the system processes large amounts of data, ensuring no data loss or corruption.
- Example: Uploading millions of records to a database to test its stability.
8. What is Agile testing and the importance of Agile testing?
Agile testing is a testing approach that is aligned with the Agile software development methodology, which emphasizes collaboration, continuous feedback, and rapid iteration.
In Agile testing, testing is integrated into the development process and performed iteratively and continuously throughout the development lifecycle. Agile testing involves the entire team, including developers, testers, and stakeholders, to ensure that the released app meets the customer's requirements and is of high quality.
The importance of Agile testing lies in its ability to catch defects early in the development cycle, giving teams ample time to troubleshoot. It also allows the application to be tested continuously throughout the development cycle, enabling teams to respond quickly to changing customer requirements and feedback.
9. What is the difference between TDD vs BDD?
TDD (Test-Driven Development) is a coding approach that ensures software is testable from the start. Developers write tests before writing the actual code, leading to cleaner, more maintainable software.
BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) focuses more on designing software from the end-user’s perspective. It translates technical concepts into plain English, making it easier for non-technical stakeholders to understand.
Below is a table for quick comparison:
|
TDD |
BDD |
|
|
Definition |
Start software development by writing test cases |
Use given-when-then syntax to:
|
|
Goal |
Test coverage and code testability |
Alignment between technical and business stakeholders |
|
Test writing |
Developers |
Varies on the team context. The ideal scenario is normally:
|
|
Tools |
Test libraries: JUnit, NUnit, TestNG, Selenium Testing tools: Katalon, TestComplete |
Available frameworks: Cucumber, SpecFlow and Behave. |
Read More: TDD vs BDD: A Comparison
10. What is Data-driven Testing?
Data-driven testing is a design pattern to reuse the same test flow against multiple sets of data.
|
Scenario: Login
|
Test case |
Data input |
|
Test Case 1 |
Valid username and password combos |
|
|
Test Case 2 |
Invalid username and password combos |
The point of data-driven testing is not hard-coding and limiting tests to a single input value. Instead, you’ll be parameterizing and using global variables for your test to read directly from databases, spreadsheets, or XML files.
Data-driven testing is particularly useful for:
- Input validation
- Boundary testing
- Error handling and exception testing
- Compatibility testing with different browsers, devices and operating systems configurations
- Performance testing with different data loads
Read More: A Guide To Data-driven Testing
11. What is performance testing?
Performance testing evaluates the system's performance (i.e. responsiveness, scalability, stability, and speed) under varying workload conditions. Its goal is to determine how the application behaves under normal and peak usage scenarios, such as high user traffic, large data volumes, or simultaneous user interactions.
The results of performance testing will be used to identify and resolve bottlenecks, optimize system performance, and enhance the user experience.
Read More: Performance Testing vs Load Testing
12. What is accessibility testing?
Accessibility testing is the process of evaluating a software application or website's usability for all users, including people with disabilities, such as visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments. It tests the app’s compatibility with assistive technologies such as screen readers, magnifiers, and voice recognition software.
13. Compare manual testing vs automated testing? Should teams move from manual testing to automated testing?
|
Aspect |
Manual Testing |
Automated Testing |
|
Definition |
Testers manually perform actions (e.g., open browser, set texts) to interact with the application-under-test. Tests are written in text editors on Xray, test management tools or spreadsheets. |
Testers outline interactions with the application-under-test then write an automation script to execute those actions. These test scripts can be scheduled to run on-demand and continuously optimized. |
|
Cost |
Investment in human testers. This offers lower upfront costs but is hard to scale in the future. |
Investment in developers/automation engineers and tools for test automation, CI, test management and defect tracking. |
|
Test Coverage |
Low |
High |
|
Reusability |
Test content cannot be easily reused |
Test content can be reused easily:
|
|
Types of Testing |
Exploratory testing Usability testing Ad hoc testing |
Regression testing Integration testing Data-driven testing Performance testing |
If the testing effort is repetitive and requires frequent regression testing, QA teams should consider automation testing. However, manual testing still has its value in ad-hoc testing or exploratory testing, so the decision really depends on the type, goal, and complexity of the project. Here is a guide to move from manual testing to automation testing.
Read More: 15 Different Types of QA Testing
14. Compare black-box testing vs white-box testing
|
Black-box Testing |
White-box Testing |
|
|
Definition |
Write tests without access and visibility to an application's internal workings and code structure |
Write tests with full access and visibility to an application's internal workings and code structure |
|
Goal |
Testing for user experience, security, and compatibility |
Testing for code quality and optimization |
|
Testing levels |
UI E2E testing Compatibility testing |
Unit testing Integration testing Static code analysis |
|
Tester |
Business stakeholders Test engineers (manual or automated) |
Developers |
15. Explain end to end testing in your own words. Compare End to End Testing vs Integration Testing
End-to-End testing checks the entire application to ensure all parts work together as expected, just like a real user would experience. It tests everything from the front end to the back end, including databases, APIs, and third-party services.
|
Aspect |
End-to-End Testing |
Integration Testing |
|
Scope |
Tests the entire system from start to finish. |
Checks how different modules work together. |
|
Purpose |
Ensures the full application functions correctly. |
Verifies data flow between connected components. |
|
Example |
Testing a complete online shopping process. |
Checking if the payment gateway communicates with the checkout page. |
Top QA Tester Interview Questions And Answers
The list above includes fairly common QA interview questions that anyone in the industry can face in interviews. In this section, we provide you with QA Interview questions specifically tailored for QA testers.
QA testers are professionals responsible for executing test cases, identifying and documenting defects, and providing feedback to the development team. They are usually asked technical questions aiming to uncover their understanding of the testing activities and automation testing best practices.
16. How do you perform visual testing?
Visual testing can be performed manually, where the tester checks the application visually for inconsistencies. This can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
Many testers employ the Image Comparison technique, which involves capturing screenshots of the UI elements in a baseline state, then comparing them with screenshots of the actual UI to see if there are any unintended visual changes.
However, even this approach is not the best. There are so many factors that may cause false positives in visual testing. Using visual testing tools can reduce false positives and make the process more efficient.
Read More: How Automated Visual Testing Will Redefine the Testing Pyramid
17. How do you prioritize test cases for execution?
There are many criteria to consider when prioritizing test cases for execution. Below is a list of 9 most common criteria QA professionals use:
- Business impact: test cases that are verify critical flows (e.g., Login, Checkout)
- Risk (test cases of high-risk areas in the app)
- Frequency of use (test cases for features used by large numbers of users)
- Dependencies
- Complexity
- Customer or user feedback (test cases that address customers’ pain points)
- Compliance requirements (test cases covering regulations specific to the industry)
- Historical data (test cases that have historically resulted in defects or issues)
- Test case age (old test cases may require updates and maintenance)
Read More: A Complete Guide To Choose Test Case For Automation
18. What are the key components of a good test case?
- Know when manual or automated testing would be best
- Use appropriate design method (e.g., data-driven testing) for different requirements and scenarios
- Test cases should be designed to be scalable and reusable, so that they can be leveraged across different testing cycles or projects to save time and effort.
- Each test case should have a unique identifier or name to make it easy to reference and filter for regression testing
- Test data inputs should cover happy and negative inputs to uncover edge cases
- Tests should run on environments (browser, device and operating system) that end-users use the most
- They should be stored in a centralized repository or test management tool to allow for easy access, maintenance, and reporting.
- QA testers should design independent test cases, so that the execution of one test case does not impact the results of another.
19. What are defect triage meetings?
Defect triage meetings are used to prioritize and assign defects to the appropriate team members. During defect triage meetings, QA testers present the defects identified during testing, including their severity and priority, and discuss the potential impact of the defects on the project.
20. Can you provide an example of a particularly challenging defect you have identified and resolved in your previous projects?
There is no true answer to this question because it depends on your experience. You can follow this framework to provide the most detailed information:
- Step 1: Describe the defect in detail, including how it was identified (e.g., through testing, customer feedback, etc.)
- Step 2: Explain why it was particularly challenging.
- Step 3: Outline the steps you took to resolve the defect, including any collaboration with developers or other team members.
- Step 4: Discuss any obstacles or roadblocks you encountered.
- Step 5: Explain how you verified that the defect was fully resolved and the impact it had on the project and stakeholders.
- Step 6: Reflect on what you learned from this experience.
21. Explain API Testing and show your approach to API Testing
API testing is key because almost every application type is heavily reliant on APIs. The UI and API are interlaced, making it even more critical to understand how data and logic processes from one layer to the other.
Here are what to consider when designing an API test:
- Read the API documentation: understand the specifications for functionalities and technologies of the APIs to write test cases with clear objectives
- Architectural style: schemas written in REST, GraphQL and SOAP differ in concepts and implementation which makes testing them different as well
- Automate data-driven tests: let API flows parse through various data types, formats, structures, and scenarios
- End-points management: avoid duplicating or missing scenarios by grouping API/web services endpoints
22. How do you ensure that test cases are comprehensive and cover all possible scenarios?
Although it is not always feasible to cover ALL possible scenarios, testers should try to venture beyond the happy path i.e. testing the app under normal conditions.
Apart from the common test cases, QA testers also need to consider edge cases, and negative scenarios, which are test scenarios that involve unusual or unexpected inputs or usage patterns. Attackers are more likely to exploit non-standard scenarios, so including such scenarios in your test plan is a great way to improve test coverage.
23. What is your approach to identifying and reporting defects?
Many QA testers follow these steps to identify and report newly found defects:
- Replicate the defect and gather relevant information such as steps to reproduce, screenshots, logs, and system configurations.
- Assign a severity level to the defect based on its impact on the application and users.
- Log the defect in a tracking tool with a clear description, expected vs. actual results, and steps to reproduce.
- Communicate the defect to the development team and collaborate with them to identify the root cause and potential solutions.
- Continuously follow up on the defect until it is resolved and verified to be fixed.
24. How do you measure the effectiveness of your testing efforts?
There are several testing metrics to consider:
- Test case execution rate
- Test coverage
- Defect density
- Defect rejection rate
- Mean time to failure (MTTF)
25. What are test management tools?
Test management tools are used by testing teams to manage and organize their testing activities. These tools provide features to manage test cases, test plans, test execution, and test reporting.
Top QA Manager Interview Questions
QA interview questions for managers usually focus more on leadership, strategy, and management skills, sometimes even on compliance standards if you are in a highly regulated industry like BFSI or Healthcare. For technical QA interview questions, you can refer to the previous section. In this section, we will go over management-focused questions.
26. Describe a situation where you had to make a difficult decision in managing a testing team, and how you handled it.
This is a situational question, and of course, there is no correct answer. You can use the STAR method to ensure that your answer provides the information your interviewer wants to hear:

27. How do you ensure that the testing team is aligned with the development team and the product roadmap?
- Regular communication between testing and development teams
- Collaborative refinement of user stories
- Agreement on common testing methodologies and standards
- Integration of testing activities into the overall development process
- Continual review and adjustment of testing priorities based on changes to product roadmap or development progress
28. What is your experience with implementing an automation testing tool?
- Identify areas for automation testing and prioritize them based on impact
- Evaluate and select appropriate automation testing tool based on technical requirements
- Define KPIs and success criteria for automation testing and establish continuous monitoring and reporting mechanism
- Train testing team on automation tool and test plan and establish necessary governance, policies, and procedures
- Track automation testing tool effectiveness and make adjustments if needed
29. How do you leverage your technical knowledge and experience to guide your team in identifying and resolving complex testing issues and challenges?
QA Managers are not just managers. They used to be testers, and their subject expertise makes them a valuable asset to the team whenever roadblocks arise. QA managers should also collaborate with cross-functional teams, including development and product teams, to identify and resolve issues that impact the product's quality.
With their skills, QA managers usually take on high-level analysis and make data-driven decisions based on testing reports to best improve testing efficiency and effectiveness.
30. How do you manage your QA team?
This question is designed to learn more about your management style. Not just in QA, managers in any industry need to have good communication skills, empathy to understand diverse perspectives, good leadership skills to connect a diverse group of testers together, and have accountability for the performance of the whole team.
General QA Interview Questions
There are also other common questions that the interviewer might ask to learn about you, your personality, and your understanding of the company. Have a look at these general QA interview questions and prepare in case you are asked. They are not tricky questions, and you can easily answer them on the spot:
- What are your key strengths? Also, share a weakness and explain how you plan to address it.
- How did you learn about this job opportunity?
- Why are you interested in this position?
- What is your ideal job?
- Describe yourself using three adjectives.
- What do you enjoy doing outside of work?
- Why should we hire you as a QA tester/QA analyst/QA manager?
- What type of work environment do you prefer?
- Who has influenced your career the most?
- What are your career goals for the next five years?
QA Interview Questions On Background And Work Experience
They are QA interview questions that allow interviewers to take a deep-dive into your professional life. These questions come after the general questions. Try to give a more detailed answer, and demonstrate your professionalism. Showcase who you are in a work setting.
- Can you tell us about your background and experience in QA?
- What brought you to a career in QA?
- What do you think were your biggest achievements in your QA career?
- Have you worked on any challenging QA projects? Can you describe them in detail?
- Can you show us your thought process when you resolve this specific testing problem?
- How do you handle and prioritize multiple testing projects at once?
- Can you give an example of a bug you found that required extensive communication with the dev team?
- Are you familiar with any automation testing tools? How do you use them in your daily work?
- What are some recent advancements or updates in QA technology that you know?
- Can you describe a situation where you collaborated with developers or other teams to resolve a testing issue?
Tricky QA Interview Questions
These QA interview questions go beyond textbook knowledge—they focus on real-world problem-solving. Interviewers, especially experienced QA testers, can easily tell whether a candidate has encountered these situations firsthand.
How to Answer Effectively:
- Use the provided answers as references, but incorporate your own experiences for authenticity.
- Apply the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to structure your responses.
- Be specific and demonstrate your thought process—how you approach problems matters more than just having the correct answer.
- What is your approach when you encounter a scenario where the requirements are incomplete or missing?
- How do you handle testing in situations where there is a tight deadline?
- Can you explain how you would test a complex software system with limited documentation?
- What are some of the most common technical problems in software testing?
- How do you ensure compatibility of a web application with multiple browsers and devices?
Recommended Readings For Your QA Interview
The list above only touches mostly the theory of the QA industry. In several companies you will even be challenged with an interview project, which requires you to demonstrate your software testing skills. You can read through our Katalon Blog for up-to-date information on the testing industry, especially automation testing, which will surely be useful in your QA interview.
As a leading automation testing platform, Katalon offers free Software Testing courses for both beginners and intermediate testers through Katalon Academy, a comprehensive knowledge hub packed with informative resources.

Katalon Academy offers short-form, easy-to-digest video courses for beginners, and in-depth guides on the Katalon platform for advanced learners. It also offers courses focused on specific testing types, such as API, desktop, mobile, or web testing, to cater to the specific needs of QA professionals. The platform is continually updated to keep up with the latest trends, and experienced testers can even have a look to keep their knowledge up-to-date.
In addition to all of this, to better prepare for your interviews, here are some topic-specific lists of interview questions:


